z80count
This is a simple tool that parses Z80 assembler using regular expressions (I know!) and adds comments to the code with the cycles used by the instruction.
It needs testing and probably a proper Z80 parser, but it works for me and the Z80 assembler syntax I use.
Installation
To install for production you can use pip:
pip install --user z80count
Or you can download the package from z80count's releases tab, unpack and run:
python setup.py install
To install for developmet run:
git clone https://github.com/reidrac/z80count.git
cd z80count
pip install -e ".[dev]"
Usage
You can use it with:
z80count.py < file.asm > file_c.asm
Or inside vim you can:
:% !z80count.py -su
With -s the tool adds a subtotal to the comments and -u tries to update
existing comments generated by the tool.
Example:
push hl
pop bc
ld hl, $5800
ld e, 7
.fade_out_all_loop0
push hl
push bc
halt
.fade_out_all_loop1
ld a, (hl)
and 7
jr z, no_fade_all_ink
dec a
.no_fade_all_ink
ld d, a
ld a, (hl)
and $38
jr z, no_fade_all_paper
sub 8
.no_fade_all_paper
or d
ld d, a
ld a, (hl)
and $c0
or d
ld (hl), a
inc hl
dec bc
ld a, b
or c
jr nz, fade_out_all_loop1
pop bc
pop hl
dec e
jr nz, fade_out_all_loop0
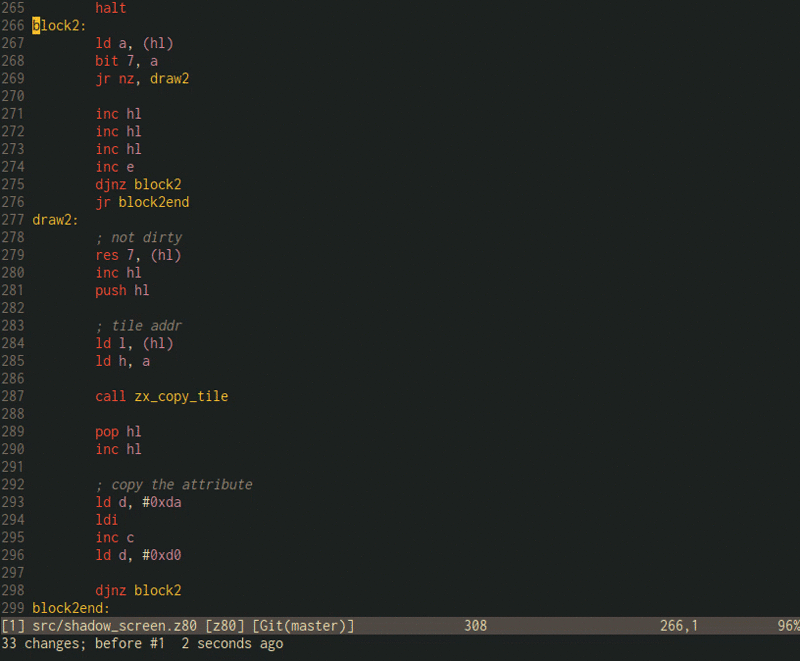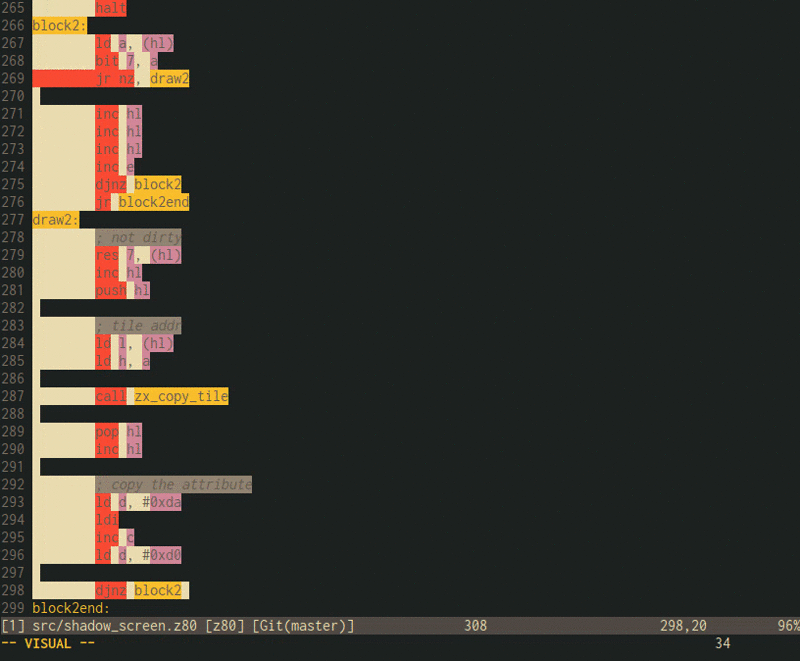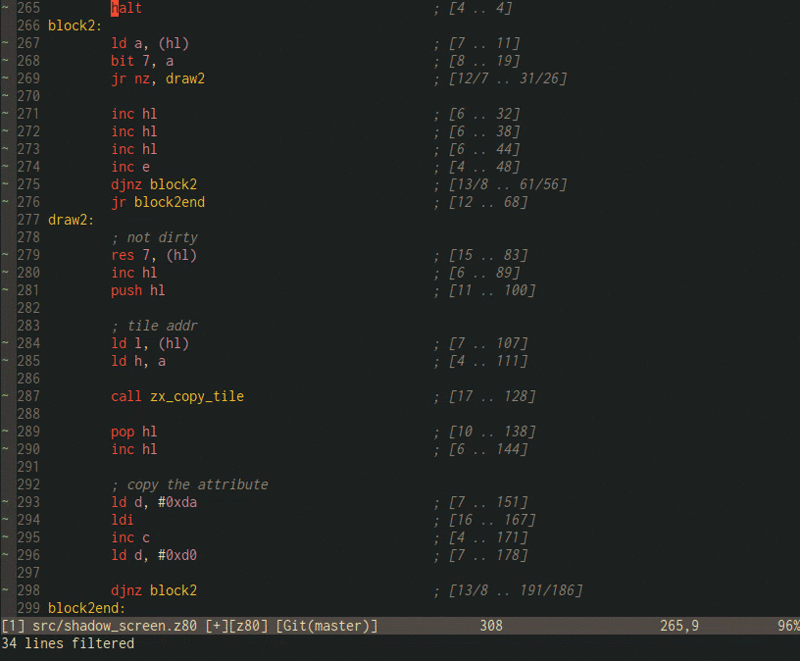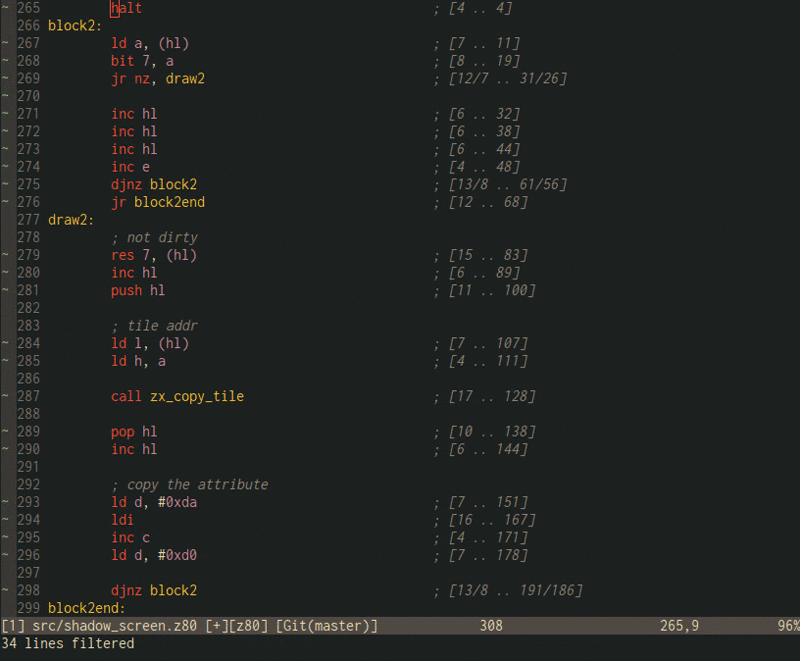
Processed with z80count.py -s results in:
push hl ; [11 .. 11]
pop bc ; [10 .. 21]
ld hl, $5800 ; [10 .. 31]
ld e, 7 ; [7 .. 38]
.fade_out_all_loop0
push hl ; [11 .. 49]
push bc ; [11 .. 60]
halt ; [4 .. 64]
.fade_out_all_loop1
ld a, (hl) ; [7 .. 71]
and 7 ; [7 .. 78]
jr z, no_fade_all_ink ; [12/7 .. 97/85]
dec a ; [4 .. 89]
.no_fade_all_ink
ld d, a ; [4 .. 93]
ld a, (hl) ; [7 .. 100]
and $38 ; [7 .. 107]
jr z, no_fade_all_paper ; [12/7 .. 126/114]
sub 8 ; [7 .. 121]
.no_fade_all_paper
or d ; [4 .. 125]
ld d, a ; [4 .. 129]
ld a, (hl) ; [7 .. 136]
and $c0 ; [7 .. 143]
or d ; [4 .. 147]
ld (hl), a ; [7 .. 154]
inc hl ; [6 .. 160]
dec bc ; [6 .. 166]
ld a, b ; [4 .. 170]
or c ; [4 .. 174]
jr nz, fade_out_all_loop1 ; [12/7 .. 193/181]
pop bc ; [10 .. 191]
pop hl ; [10 .. 201]
dec e ; [4 .. 205]
jr nz, fade_out_all_loop0 ; [12/7 .. 224/212]
Comments show subtotals, and there are two types:
- [A .. T0]
- [B/A .. T1/T0]
Where A, B, T0 and T1 are: - A is the number of cycles of current instruction. In case of a conditional instruction, this is the value when the condition is not met. - B is the number of cycles of current instruction when the condition is met. - T0 is the subtotal when the conditional is not met. - T1 is the subtotal when the conditional is met.
Troubleshooting
Here be dragons!
Use -d flag if you think one instruction is not correctly parsed.
Feel free to open a PR if you find a bug!
Authors
- Juan J. Martinez jjm@usebox.net
- Alexis Roda (https://github.com/patxoca)
